When it comes to getting your ears pierced, it’s not just about picking the prettiest earrings – there are some potential issues to be aware of. In this blog, your ENT doctor in Palawan will discuss some possible problems that can pop up during this stylish journey.
The Piercing as a Foreign Object
Getting your ears pierced involves putting in an earring, typically made of metal or plastic, which is essentially a foreign object introduced into the ear tissue. Your body’s natural response is to react to this foreign element – it might try to push the earring out, leading to potential problems like infection or rejection. As your ear heals, the body forms tissue around the earring, creating a protective barrier in response to this foreign presence. This encapsulation process is like the body’s way of adapting to and dealing with the introduced earring.

Embedded or Dislodged Piercings
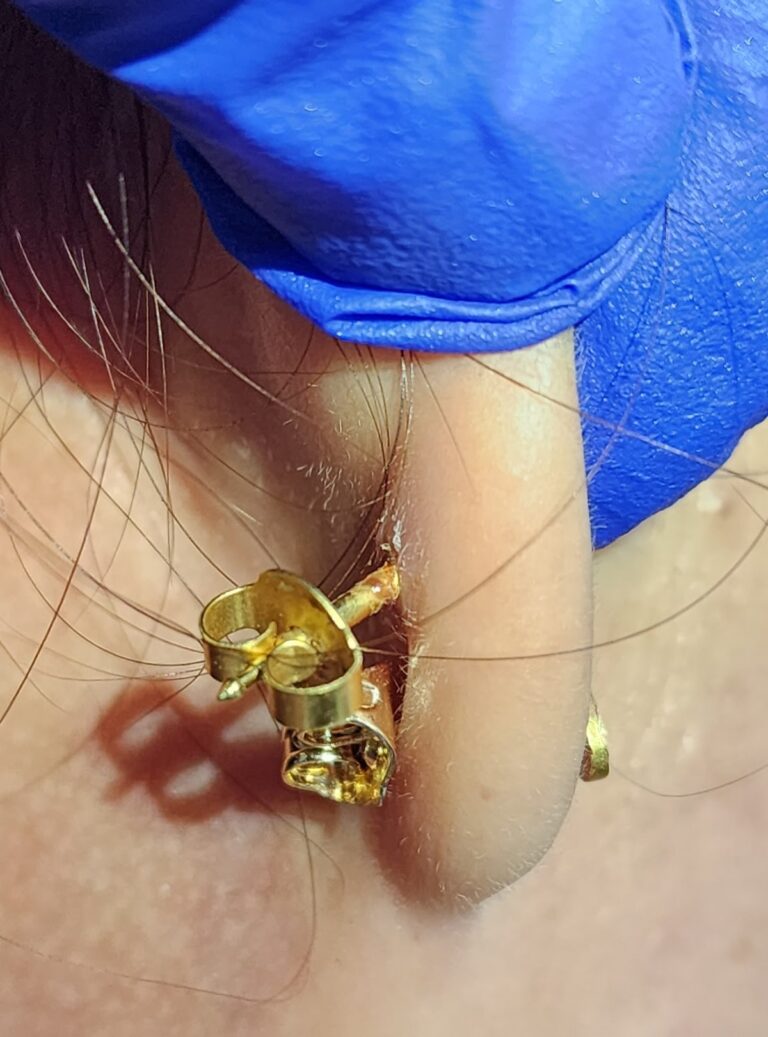
Embedded earrings occur when the earring becomes lodged within the skin due to improper sizing or tight backs. Treatment involves seeking professional help from an ENT doctor, who can safely remove the embedded earring to prevent further complications. Prevention measures include choosing appropriately sized earrings and avoiding overly tight backs.Extruded earrings, where the body attempts to push out the foreign object, may be caused by the use of low-quality materials or improper aftercare. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause, and prevention includes selecting high-quality earrings and following recommended aftercare practices to minimize the risk of extrusion.
Piercing Infection
Ear piercing infections can arise from bacteria entering the pierced area, often due to inadequate aftercare practices or the use of contaminated instruments. Complications of an ear piercing infection may include redness, swelling, warmth, and discharge from the pierced site.
Consulting an ENT doctor near you is crucial to prevent complications like the spread of infection to surrounding tissues or the development of abscesses like in the picture. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antibiotics prescribed by your ear doctor coupled with proper wound care.
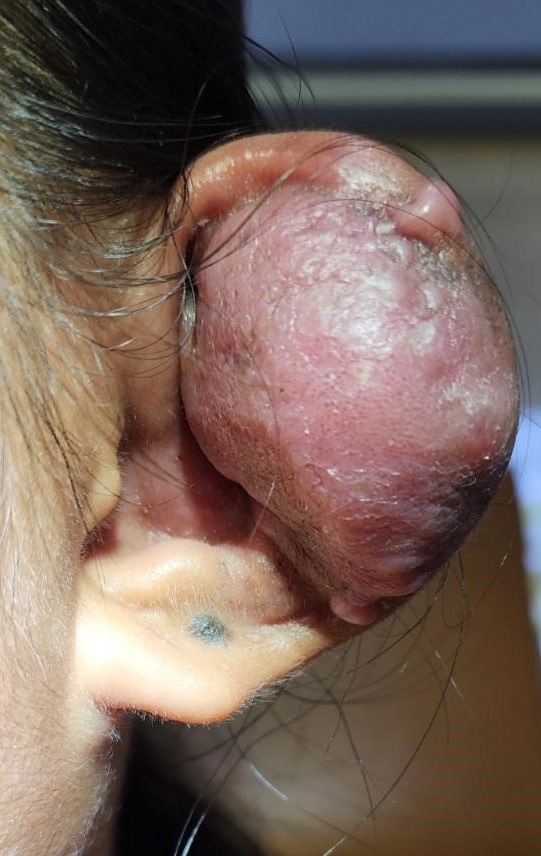
Prevention strategies include meticulous aftercare routines, avoiding touching the piercing with unwashed hands, and selecting high-quality, hypoallergenic earrings. Regular check-ups your ENT doctor can also help identify and address any potential issues before they escalate into infections.
Keloids
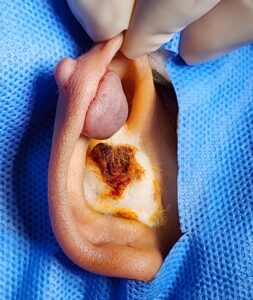
Keloids are raised scars from any wound.
Keloids are basically your healing going haywire: the body’s healing response going into overdrive. This overproduction causes raised scars, often extending beyond the original wound. While a certain amount of collagen is necessary for wound healing, in the case of keloids, it becomes excessive, resulting in a characteristic raised and sometimes larger-than-expected scar.
Keloids can occur in response to ear piercing, particularly in individuals with a genetic predisposition. Not everyone is equally prone to keloids, but certain areas of the ear, such as the cartilage, are more susceptible. To avoid keloids, it’s essential to choose appropriate jewelry, avoid excessive pressure on the piercing, and practice diligent scar care. Treatment options for existing keloids may include steroid injections, silicone sheets, or surgical removal, but prevention through careful aftercare remains key to minimizing the risk. Following aftercare instructions by your piercer, as well as early consultations with a an ENT doctor near you can help avoid keloids after ear piercing
Consulting the best ENT specialist is crucial to prevent complications like extrusion, infection, and keloid formation in ear piercings, ensuring optimal outcomes and patient safety. Your ENT doctor can minimizes piercing risks and promote successful healing for your ears.
Experience expert ENT surgical care tailored to your needs.
Book now to schedule your appointment with a skilled ENT surgeon near you and take the first step towards a healthier you.
Your well-being is our top priority.

