A 17-year-old patient came into the clinic with an inner lip mass, around 3 millimeters by 5 millimeters. It started 2 years ago when he was eating hurriedly and bit into his inner lip. Since then, the mass would increase and decrease in size and occasionally bleed when he bites it. He came to consult an ENT doctor in Palawan to see if the mass can be removed.
What Is an Inner Lip Mucocele?
An inner lip mucocele is a type of cyst that forms on the inside of the lip due to a blocked or damaged salivary gland. These cysts are usually filled with mucus and can vary in size. They often appear as a soft, bluish, or clear lump and can be quite bothersome, especially if they fluctuate in size or become irritated frequently. Understanding what a mucocele is can help in recognizing the condition early and seeking appropriate treatment from an ENT doctor.
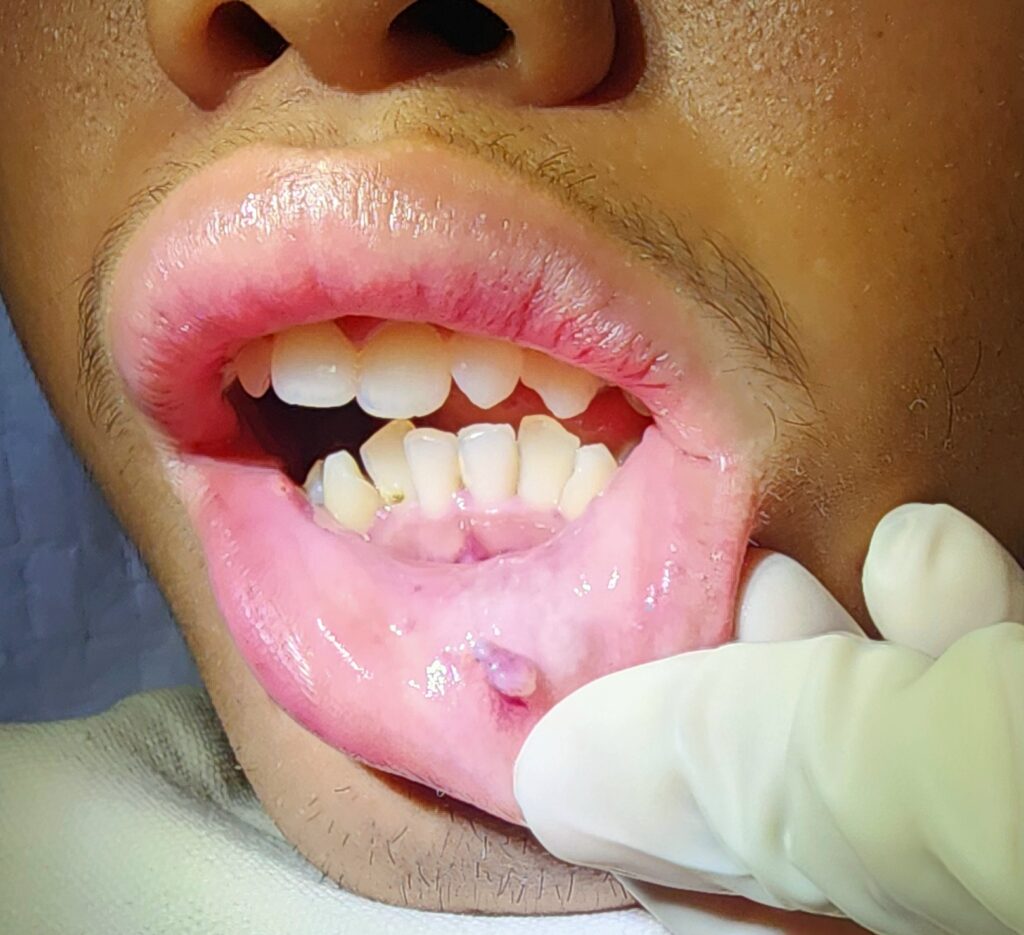
The mucous cyst forms when the salivary gland duct gets blocked, either from trauma, such as a lip bite, or from chronic irritation. When the gland is damaged, mucus pools in the surrounding tissues, forming a lump. Although mucoceles are generally benign, they can be persistent and sometimes troublesome.
Causes and Symptoms of Inner Lip Mucocele
Inner lip mucoceles typically occur due to trauma or injury to the lip, such as accidental biting, as in the case of our 17-year-old patient. Other causes include blockage of salivary gland ducts and chronic irritation from habits like lip biting or sucking.
Common symptoms include a painless, soft, and smooth bump inside the lip. These cysts can fluctuate in size, occasionally bleed if bitten or irritated, and cause discomfort or annoyance due to their presence. Some patients may experience a bluish tint in the affected area, making the mucocele more noticeable.
Treatment Options for Inner Lip Mucocele
Treatment for inner lip mucoceles can vary based on the severity and persistence of the cyst. In many cases, mucoceles resolve on their own without treatment. This spontaneous resolution happens when the blocked duct opens up and the mucus is reabsorbed by the body.
For those mucoceles that do not resolve on their own, there are several home remedies and medical treatments available. Home remedies, such as applying a warm compress to the area, can help reduce swelling and discomfort. The heat from the compress increases blood flow to the area, promoting healing.
Medical treatments may include corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation or aspiration to drain the cyst. Corticosteroid injections can help shrink the cyst by reducing the inflammatory response, while aspiration involves using a needle to remove the fluid from the cyst. Both treatments are typically performed by an ENT doctor in an outpatient setting.
Is Surgery Needed for an Inner Lip Mucocele?
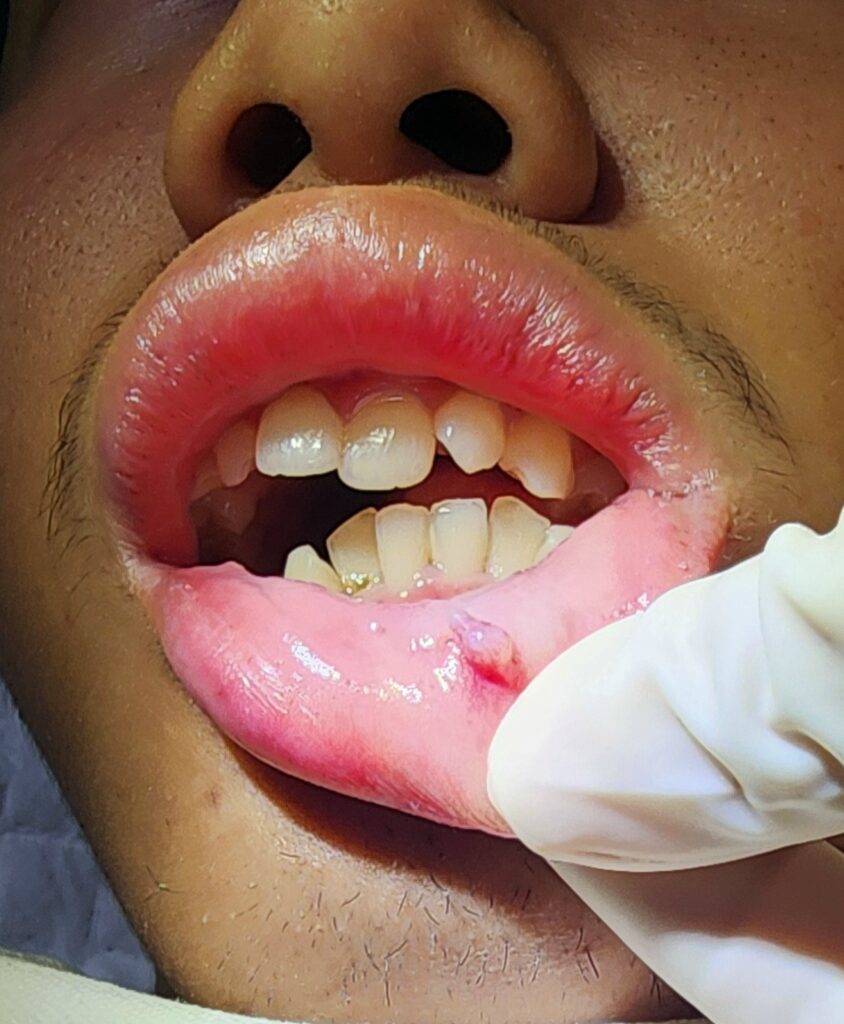
Surgery is often considered when the mucocele is persistent and does not resolve on its own, repeatedly gets irritated, increases in size, or bleeds frequently. If the cyst causes significant discomfort or interferes with daily activities, an ENT doctor will evaluate the condition and recommend surgery. Surgical removal typically involves excising the cyst and the affected salivary gland to prevent recurrence.
The decision to opt for surgery will depend on the patient’s specific circumstances and the ENT doctor’s assessment. While surgery is generally effective, it is usually reserved for cases where other treatments have failed or when the mucocele causes significant issues.
In the case of the patient above, the patient was offered to have conservative management. However, due to the bleeding of the mass when he bites into it, he decided to have it removed.
When to Consult an ENT Surgeon
If you suspect you have a mucocele or have noticed a persistent lump in your inner lip, consult with an ENT doctor near you. This can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment, preventing potential complications.
Patients should seek help if the mucocele does not resolve on its own within a few weeks, if it frequently gets irritated or bleeds, or if it causes significant discomfort. Additionally, any changes in the size, color, or sensation of the cyst warrant a visit to an ENT doctor.
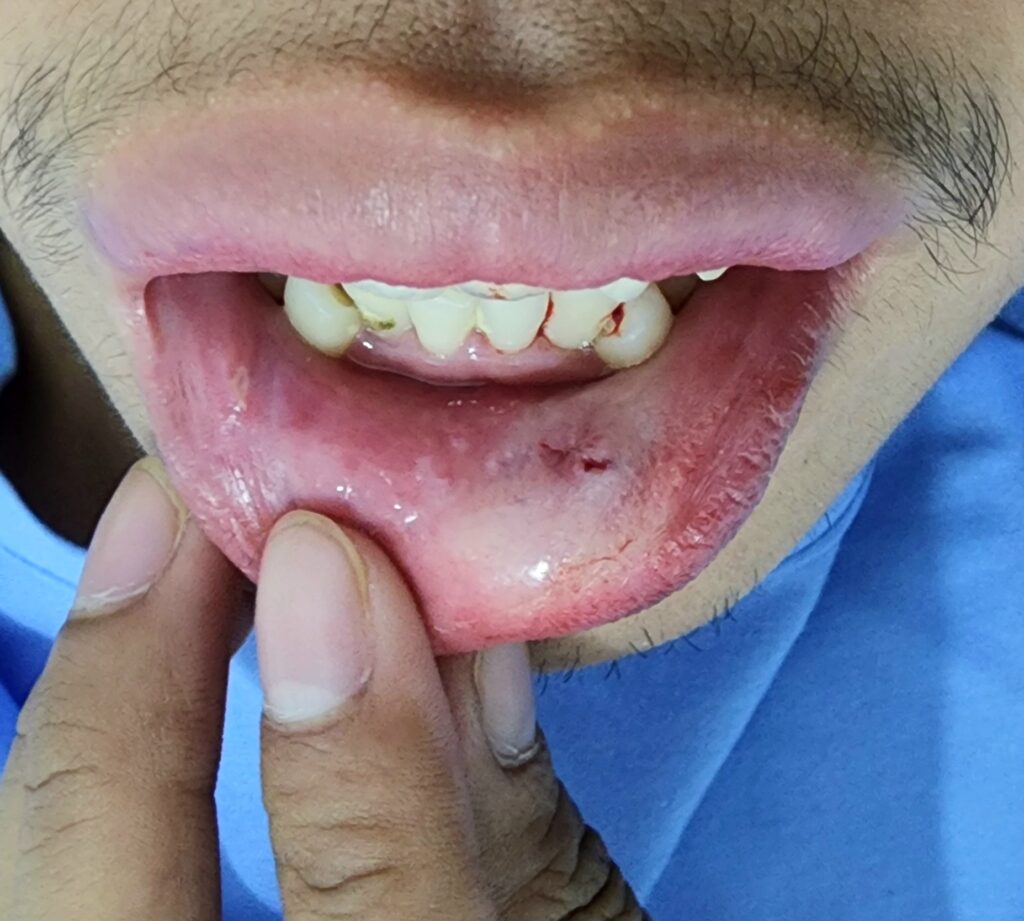
In conclusion, inner lip mucoceles, while often benign, can be a source of discomfort and inconvenience. Consulting an ENT doctor can help determine the best course of action, whether it be surgical or non-surgical, to effectively manage and treat this condition. If you have any concerns about a lump in your lip or any other ENT-related issues, don’t hesitate to contact an ENT surgeon near you for expert advice and treatment.
Experience expert ENT surgical care tailored to your needs.
Book now to schedule your appointment with a skilled ENT surgeon near you and take the first step towards a healthier you.
Your well-being is our top priority.

