What is a salivary duct stone?
A sialolith is a small, hard stone that forms in the salivary gland or salivary duct. It is the most common benign cause of swelling of the salivary glands. It occurs in approximately 1 in every 10,000 to 30,000 people. Consultation with an ENT doctor is important if you have any mouth swelling.
The salivary glands are located in the mouth and produce saliva. Saliva helps to moisten and lubricate the mouth, aid in digestion, and protect against tooth decay. Three main pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, the submandibular glands, and the sublingual glands. Stones may form in in the ducts of any of these salivary glands.
Are you at risk for developing a sialolith?
Sialoliths occur for many reasons, including dehydration, resulting in an excess of minerals in the saliva. These may occur in people who have limited access to water or restrooms. Examples of these are people who live on sailboats with limited supply of water or even busy office workers who forget to drink. in addition, people with decreased saliva production, such as the elderly, and those who have Sjorgens syndrome. may also be at risk for sialolithiasis. Smoking and medications that decrease saliva production or increase urination can also induce stone formation.
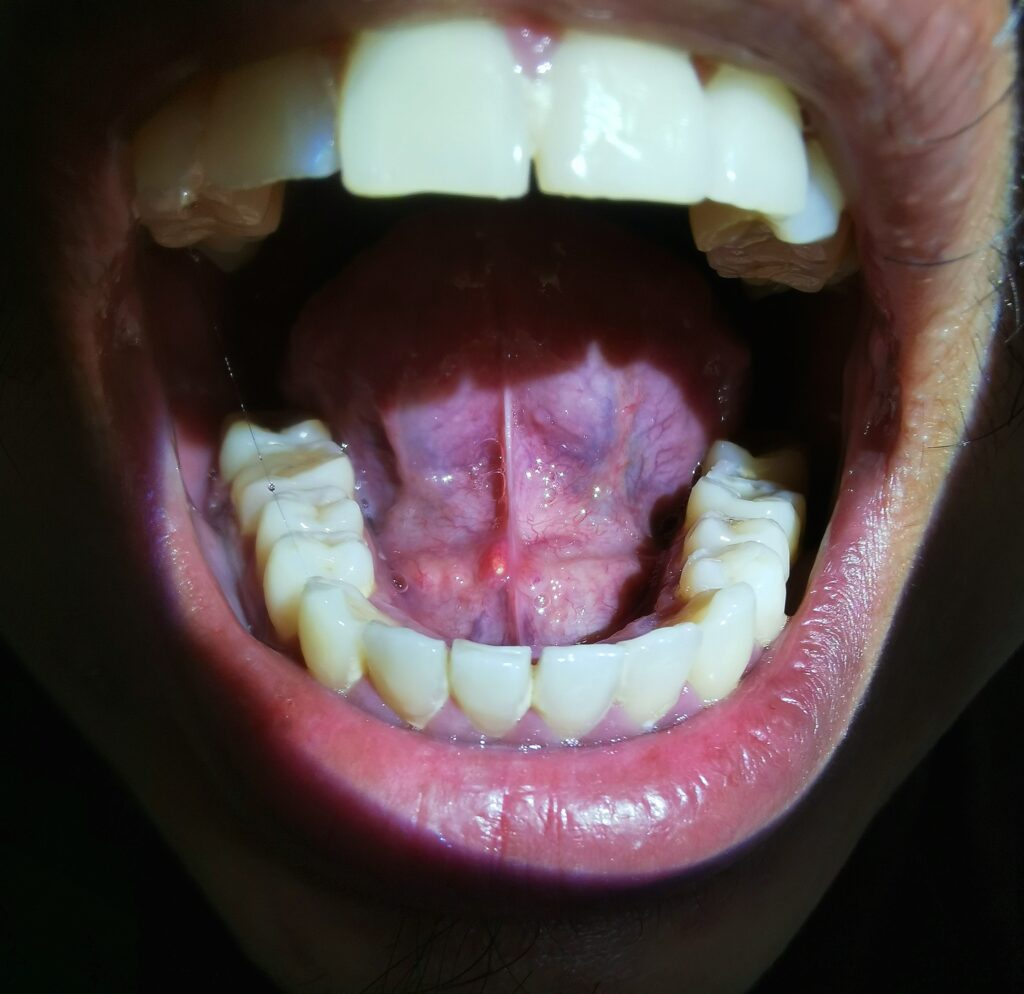
Symptoms of sialoliths?
Symptoms of a sialolith may include pain or discomfort when eating or drinking, difficulty swallowing, and swelling in the salivary gland or salivary duct. Sialoliths can sometimes be visible on the surface of the mucosa of the mouth and may be seen or felt as a small, hard lump.
Treatment of Salivary duct stones
Sialolith treatment may range from conservative to aggressive. Sometimes, your ENT doctor may just advise warm compress, and sucking on a lemon to stimulate salivary production, These conservative measures may potentially push the stone out of the duct. Your ENT doctor may also start you on antibiotics or pain medications. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the sialolith, drain any pus formation, and sometimes even re-route the salivary duct.
It is important to see an ENT doctor if you experience symptoms of a sialolith or if you notice a hard lump in your salivary gland or salivary duct. Your head and neck surgeon can diagnose a sialolith, and recommend the appropriate tests and treatment options.
In conclusion, a sialolith is a small, hard stone that forms in the salivary gland or salivary duct. It can cause pain or discomfort when eating or drinking, difficulty swallowing, and swelling in the salivary gland or salivary duct. Sialoliths may be treated with supportive therapy, medications or by surgical removal of the stone and repair of the salivary duct
Say goodbye to ear, nose, and throat discomfort with our expert ENT care.
Book now to schedule your appointment with an experienced ENT doctor near you and start feeling better today.
Your health is our priority.

